Supervisors: Jérôme Faure, Igor Andriyash (LOA) & Kristjan Põder (DESY)
LOA (Laboratoire d'Optique Appliquée) is located at 20 km south of Paris, on the Institut Polytechnique de Paris campus. LOA is a laboratory of 80 people, specialized in ultrafast and ultra-intense lasers and their applications to laser-plasma interaction at high intensity. LOA is a pioneer laboratory in Laser Wakefield Acceleration (LWFA) and has made several seminal contributions to the field of laser-driven particle acceleration and plasma-based X-ray sources.
In laser wakefield acceleration, a femtosecond laser pulse is focused in a plasma and excites a very intense plasma wave. This plasma wave carries an electric field of some 100 GV/m, which can be used to accelerate plasma electrons to GeV energies in centimeter distances only, holding the promise of a drastic miniaturization of particle accelerators. In addition, the accelerated beam properties are extremely interesting for a number of applications, such as cancer treatment or hard X-ray imaging for the industry.
Our team at LOA is currently building a new platform for developing a prototype high-repetition rate laser wakefield accelerator (LWFA) within the project LAPLACE-HC (LAser PLasma Acceleration CEnter at High repetition rate). In LAPLACE-HC, we are building a LWFA running at 100 Hz, and producing electron beams with tuneable energies in the range 10-200 MeV. The goal of this prototype is dual:
- Perform R&D to bring the performance of the LWFA to a level that is comparable with that of conventional RF accelerators, in terms of parameter stability, robustness and beam availability.
- Perform R&D to demonstrate high-repetition-rate operation of the accelerator for long periods of time, in particular to enable applications of LWFA in other fields, such as non-destructive testing for industrial applications, very high energy radiotherapy for cancer treatment, or femtosecond probing of materials with X-rays.
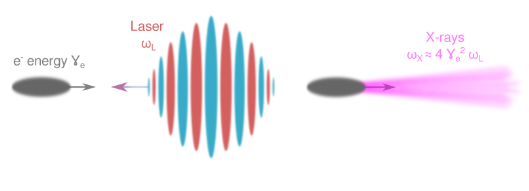
This PhD project will focus on the theoretical and numerical study of an Inverse Compton Scattering (ICS) X-ray source using the parameters of the LAPLACE-HC experiment. Such an X-ray source, running at 100 Hz and in the 100 keV energy range would be of tremendous interest for performing structural studies on condensed matter with femtosecond resolution.
Expected Results
- Theoretical study of a future ICS source with LAPLACE-HC parameters
- Start to end Particle in Cell simulations (using FBPIC) and the code Synchrad to simulate the laser-plasma accelerator and the ICS process
- Development of machine learning strategies for optimization of the ICS process
- Study of exotic schemes relying on the spatio-temporal manipulation of the colliding laser field to improve/taylor the performance of the X-ray source
Planned secondments
- 1 months at DESY (year 1): participation in ICS experiment
- 2 month at DESY (year 2): collaboration with experts on simulations of ICS process and machine learning